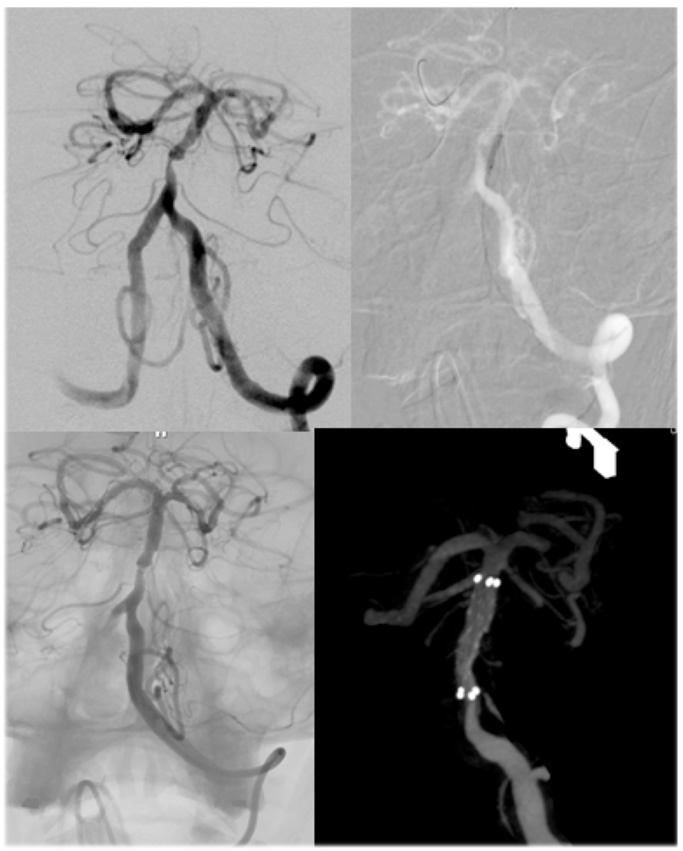
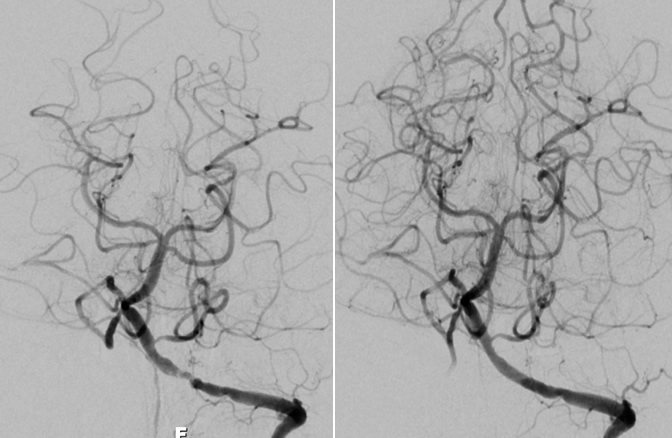
Intracranial angioplasty and stenting is performed for the treatment of stenosis (narrowing) of an intracranial artery (an artery in the brain). The narrowed artery must be causing recurrent strokes and/or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) despite the patient being on optimal medical management (on other words: optimal medical control of hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia as well as antiplatelet therapy). The procedure involves placing a small balloon and stent (metal tube) into the narrowed artery in the brain. The balloon is used to gradually open the artery and the stent is left in place to keep the narrowed artery open.